gin http从请求到响应的步骤分析
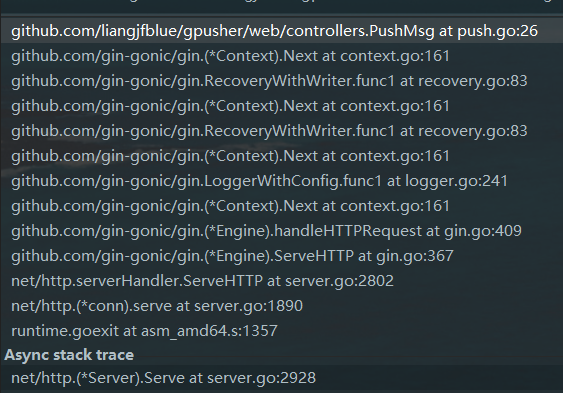
源码分析
对于gin的分析, 以以下为例子:
g := gin.Default()
g.Use(gin.Recovery())
g.NoRoute(func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(http.StatusNotFound, "The incorrect API route")
})
g.POST("/v1/push", controllers.PushMsg)
log.Fatal(g.Run(":8080").Error())
等待连接和分配goroutine
func (srv *Server) Serve(l net.Listener) error {
for {
rw, e := l.Accept()
...
c := srv.newConn(rw)
go c.serve(connCtx)
}
}
每个http请求goroutine
func (c *conn) serve(ctx context.Context) {}
服务端响应请求
serverHandler{c.server}.ServeHTTP(w, w.req)
serverHandler server的handler逻辑处理
type serverHandler struct {
srv *Server
}
func (sh serverHandler) ServeHTTP(rw ResponseWriter, req *Request) {
handler := sh.srv.Handler
if handler == nil {
handler = DefaultServeMux
}
if req.RequestURI == "*" && req.Method == "OPTIONS" {
handler = globalOptionsHandler{}
}
handler.ServeHTTP(rw, req)
}
gin路由Engine
func (engine *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
...
engine.handleHTTPRequest(c)
}
gin http handle处理请求
func (engine *Engine) handleHTTPRequest(c *Context) {
...
t := engine.trees
//从路由树中查找出请求路径和方法对应注册的响应函数
value := root.getValue(rPath, c.Params, unescape)
if value.handlers != nil {
...
//遍历顺序调用, 因为可注册一些中间件,拦截器什么的
c.Next()
return
}
}
Next只能在中间件内部使用, 主要负责注册的中间件链式调用
func (c *Context) Next() {
c.index++
for c.index < int8(len(c.handlers)) {
c.handlers[c.index](c)
c.index++
}
}
真正的/v1/push 注册的响应函数PushMsg
func PushMsg(c *gin.Context) {
...
}
总结
- 0.启动服务器
- 1.accept等待连接到来
- 2.连接来了, 分配一个goroutine来负责本次的请求 go serve()
- 3.路由判断(默认, 还是自定义路由[实现了ServeHTTP的都可以作为路由])
- 4.gin路由Engine的ServeHTTP
- 5.从gin路由树中根据请求路径和方法查找对应的注册响应函数
- 6.得到注册响应函数, 遍历顺序调用中间件,直至最后的响应函数